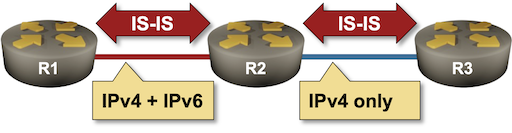
The landscape of modern networking is continuously evolving, with advancements in technology pushing the boundaries of how we interconnect devices and manage data. One key area of development has been the implementation of Dual-Stack IS-IS (Intermediate System to Intermediate System) routing protocols. This method enables networks to support both IPv4 and IPv6 traffic simultaneously, ensuring backward compatibility with older systems while allowing for the adoption of newer technologies. As networks grow in complexity and the need for more IP addresses becomes critical, understanding the intricacies of Dual-Stack IS-IS routing is becoming increasingly important for IT professionals and network engineers. In this article, we will explore the fundamentals of Dual-Stack IS-IS routing, its benefits, challenges, and its role in modern networking environments.
Understanding Dual-Stack IS-IS Routing
IS-IS is a link-state routing protocol originally designed for use in large-scale internetworking, such as those found in service provider networks. Traditionally, IS-IS supported only IPv4, but with the growing adoption of IPv6, the protocol has been extended to support dual-stack environments—meaning it can route both IPv4 and IPv6 traffic concurrently over the same network infrastructure.
In a dual-stack configuration, both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses are assigned to each network device, and routers within the network maintain separate routing tables for each protocol. However, the key challenge is ensuring seamless communication between the two IP address families. This is where Dual-Stack IS-IS routing becomes crucial, as it allows the network to handle both protocols in parallel without disrupting the existing IPv4 services.
Key Features of Dual-Stack IS-IS
- Support for Both IPv4 and IPv6: Dual-Stack IS-IS enables routers to simultaneously exchange routing information for both IPv4 and IPv6, ensuring full network interoperability.
- Seamless Migration: It allows for an easier transition from IPv4 to IPv6 by supporting both protocols on the same infrastructure, avoiding the need for complex network redesigns.
- Efficient Use of Resources: Dual-stack operation makes use of the existing IS-IS infrastructure, reducing the need for additional routing protocols or hardware upgrades.
- Improved Network Scalability: By supporting both IPv4 and IPv6, networks can scale more easily, accommodating the increasing demand for IP addresses.
Benefits of Dual-Stack IS-IS Routing
The adoption of Dual-Stack IS-IS routing brings numerous advantages to modern networking environments. Some of the most significant benefits include:
1. Simplified Network Management
One of the major benefits of Dual-Stack IS-IS is the ability to manage both IPv4 and IPv6 routing within the same protocol framework. Network operators can leverage a single protocol to handle routing for both address families, simplifying the configuration and management process. This consolidation leads to reduced operational overhead and easier troubleshooting.
2. Enhanced Network Flexibility
With Dual-Stack IS-IS, organizations can transition to IPv6 at their own pace. As IPv6 adoption continues to increase, the need for IPv4 addresses has reached its limits. However, many networks still rely heavily on IPv4 infrastructure. Dual-Stack IS-IS ensures that both address families can coexist, providing flexibility and allowing for smoother transitions to IPv6 without interrupting service for IPv4-based applications.
3. Better Performance and Reliability
Dual-Stack IS-IS enhances network performance by enabling fault tolerance. If a routing issue occurs on one protocol (e.g., IPv4), the other protocol can continue to function independently. This redundancy makes the network more reliable and resilient to failures. Additionally, the ability to simultaneously support both IPv4 and IPv6 can improve load balancing, as traffic can be routed through the best available path depending on the protocol in use.
4. Future-Proofing the Network
IPv6 adoption is steadily increasing, and while many organizations have already started migrating to IPv6, many still rely on IPv4. Dual-Stack IS-IS allows networks to prepare for future demands, including the rise of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, which often require IPv6 addresses. By integrating IPv6 support now, companies can future-proof their networks, avoiding the risks of being caught unprepared when IPv4 address space becomes fully exhausted.
Challenges and Considerations
While Dual-Stack IS-IS routing offers numerous advantages, there are also several challenges and considerations that network engineers need to address when implementing this solution.
1. Increased Complexity
Running both IPv4 and IPv6 on the same network can add complexity, particularly when managing routing tables and ensuring that both address families are properly synchronized. Engineers need to be familiar with both protocols and how they interact within the IS-IS framework. Misconfigurations or inconsistencies between the two protocol tables can lead to routing issues or traffic loss.
2. Hardware and Software Compatibility
Not all network hardware and software platforms are fully capable of supporting Dual-Stack IS-IS routing. Organizations may need to upgrade their equipment or install firmware updates to ensure compatibility with both IPv4 and IPv6. Furthermore, some legacy systems may require more significant modifications or may not be able to support dual-stack configurations at all, forcing network administrators to adopt a phased migration approach.
3. Training and Skill Gaps
Network professionals need a strong understanding of both IPv4 and IPv6, as well as how to configure and troubleshoot IS-IS routing in a dual-stack environment. In some cases, there may be a skill gap within the workforce, requiring additional training or hiring of specialized personnel. The complexity of dual-stack configurations can increase the likelihood of human error, which can have a significant impact on network stability and performance.
Best Practices for Implementing Dual-Stack IS-IS Routing
To maximize the benefits of Dual-Stack IS-IS routing, network administrators should follow certain best practices during implementation:
- Start with IPv6 Readiness: Ensure that the network infrastructure is capable of handling IPv6 traffic before enabling Dual-Stack IS-IS. This includes checking hardware compatibility, updating software, and ensuring sufficient IP address space for both protocols.
- Careful Planning of Routing Tables: Properly configure separate routing tables for IPv4 and IPv6 to prevent routing conflicts. While IS-IS can handle both address families, ensuring that each protocol has clear and distinct routing paths is crucial for stability.
- Monitor Network Performance: Regularly monitor the performance of the network after enabling Dual-Stack IS-IS to identify and address any issues promptly. Look out for potential network congestion, especially during the transition from IPv4 to IPv6-heavy traffic patterns.
- Invest in Staff Training: Ensure that network engineers are well-versed in both IPv4 and IPv6 networking principles, as well as IS-IS protocol configuration. This will help minimize the risk of configuration errors and reduce troubleshooting time in case of failures.
Conclusion
Dual-Stack IS-IS routing plays a critical role in the evolution of modern networking. As the internet transitions from IPv4 to IPv6, organizations must adopt solutions that support both address families in parallel. Dual-Stack IS-IS provides a scalable, reliable, and efficient framework for managing IPv4 and IPv6 traffic, enabling organizations to future-proof their networks while maintaining compatibility with legacy systems.
Despite the challenges, such as increased complexity and potential hardware limitations, the benefits of Dual-Stack IS-IS—such as simplified network management, enhanced flexibility, and improved performance—make it an essential tool for network engineers. With careful planning and a clear understanding of both protocols, organizations can implement Dual-Stack IS-IS successfully, ensuring their networks are ready for the future of internet connectivity.
For further reading on the technical aspects of IS-IS and its role in modern networking, check out this CIO article on IS-IS routing. For in-depth discussions on IPv6 and its impact on future networks, refer to this IPv6 Forum website.
See more Future Tech Daily